Beholding Christ in African American Art
Book Review: Beholding Christ and Christianity in African American Art, ed. James Romaine and Phoebe Wolfskill
by Victoria Emily Jones

Typically when scholars interpret African American art, they do so through the primary lens of racial identity, often glossing over overt Christian themes, expressions of religious identity. Beholding Christ and Christianity in African American Art (Penn State University, 2017), edited by James Romaine and Phoebe Wolfskill, seeks to redress that dearth by examining the Christian content, including theological significance, of works by fourteen African American artists who came to maturity between the Civil War and the civil rights era: Mary Edmonia Lewis, Henry Ossawa Tanner, Aaron Douglas, Malvin Gray Johnson, Archibald Motley Jr., William H. Johnson, James Richmond Barthé, Allan Rohan Crite, Sister Gertrude Morgan, William Edmondson, Horace Pippin, James VanDerZee, Romare Bearden, and Jacob Lawrence. Many of these artists were themselves devout Christians, working out of internalized religious convictions and not merely outward tradition or market expectations.
The essayists certainly take race into account as a factor in the works discussed, but not the only factor; political, socioeconomic, and biographical circumstances are also considered. Christianity, however, as the title suggests, is given pride of place in the selection and examination of the fifty-five images reproduced in the book.
One of the hallmarks of Beholding Christ is the diversity of styles, media, and denominational affiliations represented. As the book shows, African American art is no monolith, and neither is African American Christianity. While there is so-called primitive art and visionary art created by self-taught individuals with crayons, cardboard, or salvaged limestone, there is also neo-classical sculpture, as well as other academically informed works that tend toward impressionism or expressionism. Among the pages are rough-hewn stone sculptures, abstract watercolors, naturalistic oil paintings, and portrait photographs. While there are many depictions of Christ as black, there are also, per tradition, white Christs, and even a Middle Eastern one. What was most surprising to me was to see examples of art by African Americans from high-church traditions, like Catholicism and Anglicanism, who distinguish themselves from low-church Baptists, Pentecostals, and Holiness Christians. The editors are to the applauded for resisting the urge to perpetuate a narrow vision of “Negro art” in line with what the artists’ contemporary critics and viewers principally sought.
Another hallmark of the book is the rigorous formal evaluation and content analysis of specific artworks that make up the bulk of almost every essay, encouraging readers to look deeply. Biographical information about the artists is well integrated and does not overwhelm the focus on the works themselves. Given this image-forward approach, I must say, I’m disappointed that a handful of works, for which color photographs should be available, are reproduced in black and white—for example, Motley’s Tongues (Holy Rollers), Edward Hicks’s Peaceable Kingdom, and Lawrence’s Sermon II and Sermon VII. Luckily these can be found online, but as the entire book is printed in full color with glossy pages, I wonder why color photographs of these were not sought or obtained.
Lastly, I really appreciate the connections between artists made possible by the bringing together of these essays—some made explicitly by the authors, others implied. Douglas and Lawrence both dignified the art of black preaching by visualizing sermons. Crite and Johnson visualized the spirituals, but used very different approaches. Edmondson and Morgan were both motivated by a belief that they were divinely ordained to create by supernatural visions. Episcopal Crite and Catholic Motley intertwined class and religion in their works.
This book is essential reading for anyone in the fields of Christianity and the arts or African American studies. As one belonging to the former category, I see these artworks as part of not only art history but Christian history, and as worthy of being studied by Christians as any theological treatise, written scripture commentary, saint’s biography, or church trend. These artworks teach theology; they encapsulate hopes and fears; they comment on public issues; they expose sin; they lead us in celebration and in lament; they help us to remember the works of Christ, and invite us into communion with him; they tell us who we are and from whence we’ve come; they cast a biblically grounded vision for the future.
What follows is a brief summary of each chapter.
In chapter 1, Kirsten Pai Buick traces the network of patronage that supported Catholic sculptor Mary Edmonia Lewis, as well as the multiple geographic moves she made to further her career: from Boston to Rome (1865), Rome to Paris (1893), and Paris to London (1901). Because many of Lewis’s religious works have been lost, little attention is given in this chapter to the art itself; the only art illustration is her conventional-looking Bust of Christ (1870), mentioned cursorily in the text.
In chapter 2, James Romaine demonstrates the shift in Henry Ossawa Tanner’s paintings from the visual clarity favored by nineteenth-century academic art to a mood of personalized spiritual mystery favored by the twentieth-century symbolists. He examines four paintings as representative of this move—The Resurrection of Lazarus (1896), Nicodemus (1899), The Two Disciples at the Tomb (ca. 1906), and The Disciples See Christ Walking on the Water (ca. 1907)—revealing how each explores the complex exchange between vision and belief.

Henry Ossawa Tanner: The Disciples See Christ Walking on the Water
In chapter 3, Caroline Goeser examines the seven gouaches Aaron Douglas made in response to James Weldon Johnson’s God’s Trombones: Seven Negro Sermons in Verse. These images align biblical narrative with modern black experience to tell socially resonant stories. In its attention to the African Simon of Cyrene, for example, The Crucifixion (1927) promotes an “Ethiopianist” narrative, influenced by the late nineteenth-century biblical scholar Edward W. Blyden. Simon looms large as the most prominent figure, heaving Christ’s heavy cross over his shoulders, heroized by his vigorous stride and his active gaze toward God’s light above. Bearing similarities to that of the trudging African American migrant in Douglas’s On de No’thern Road (1926), this pose subtly associates the Great Migration north with the burdensome road to Calvary.

Aaron Douglas: The Crucifixion
In chapter 4, Jacqueline Francis examines the dozen or so paintings Malvin Gray Johnson created between 1927 and 1934, the final years of his life, as visual interpretations of Negro spirituals. Modernist in style, these paintings, she says, united old and new and high and popular expressions, helping to revive and elevate this genre of black folk music that saw diminishing audiences during the Great Depression. Swing Low, Sweet Chariot (1928), a night scene painted in thick, dark hues and mounted in a gold lunette frame reminiscent of medieval icons, received the most critical attention in Johnson’s time, eliciting comparisons to Albert Pinkham Ryder. The artist said,
I have tried to show the escape of emotion which the plantation slaves felt after being held down all day by the grind of labor and the consciousness of being bound out. Set free from their tasks by the end of the day and the darkness, they have gone from their cabin to the river’s edge and are calling upon their God for the freedom for which they long. (qtd. 56)
In chapter 5, Phoebe Wolfskill demonstrates how Archibald J. Motley Jr.’s paintings represent a middle-class bias and a subtle derision of the behaviors of the “emotional” black masses, from whom he, a Catholic, sought to separate himself. When he was young Motley moved with his family into a white Chicago neighborhood decades before the Great Migration brought working-class African Americans up north, and he studied at the prestigious Art Institute of Chicago. His membership in the Catholic Church, a large, established institution, further signaled his social standing. Wolfskill contrasts Motley’s less than empathetic treatment of demonstrative religiosity in the genre paintings Tongues (Holy Rollers) (1929), Gettin’ Religion (1936), and Getting Religion (1948) with the respectable, constrained practices of Catholic devotion suggested in his portraits Mending Socks (1924) and Self Portrait (Myself at Work) (1933).
In chapter 6, Amy K. Hamlin analyzes the formal qualities of William H. Johnson’s Jesus and the Three Marys (ca. 1939–40) and discusses the artistic and historical-cultural influences behind it. Influenced by the German expressionism Johnson encountered during his time in Europe and through his artist brother-in-law Christoph Voll, this painting holds naturalism in tension with abstraction—flattened space, an inscrutable middle form, among other elements. Hamlin suggests that Johnson chose the subject of the dead Christ in response to the increase of lynchings in the United States during the interwar period, pointing out its visual correlations to Johnson’s Lynch Mob Victim (not reproduced), which also features three female mourners.
In chapter 7, James Smalls considers the black male nude sculptures that constituted a primary focus of Richmond Barthé’s oeuvre. Such figures are rare in African American art, considered forbidden territory because of “what the exposed black body has come to signify for many African Americans—that is, a vulnerable body often exploited as a site of pain, trauma, and sexual violation—and never a body of ‘true’ agency and/or liberation” (88).
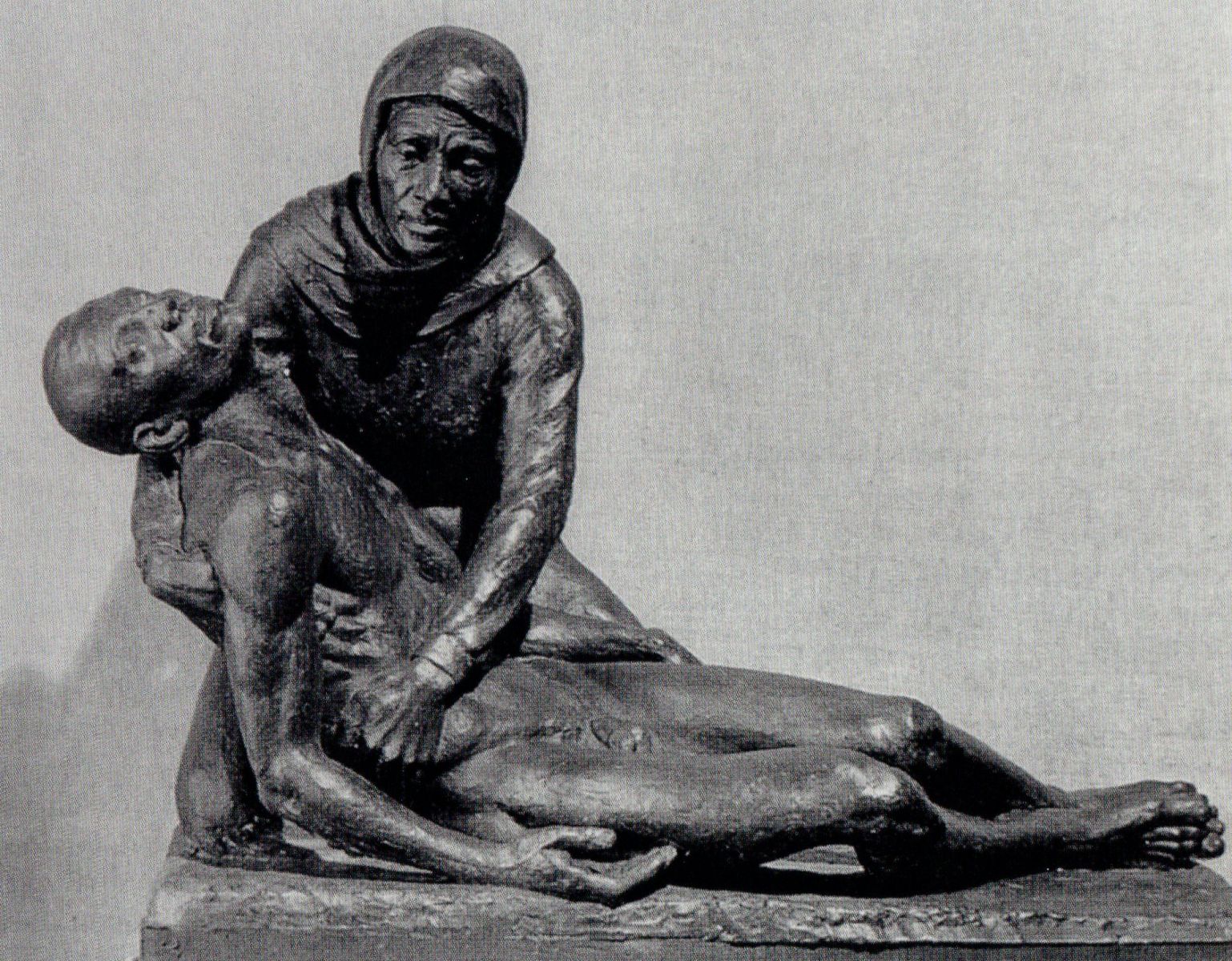

Richmond Barthé: The Mother
Smalls’s central assertion is that Catholic Barthé’s love of classical sculpture was just a pretext for indulging his homosexual desires, and that he tried to deflect his sculptures’ erotic impact by presenting their subjects in religious terms (91). This claim is, I feel, an overreach. None of the four illustrations in the chapter—Tortured Negro (1928), The Mother (1935), Birth of the Spirituals (Singing Slave) (ca. 1941), Come unto Me (1944–47)—strike me as erotic, and Smalls offers little to no support for his reading of them as such. The second, for example, shows, in Barthé’s words, a Negro mother receiving into her arms at the foot of a tree the body of her lynched son (you can see visible rope marks around his neck), in a pose that recalls the Pietà of church tradition, and yet Smalls insists it “promote[s] erotic desire” (91). He says the haggardness, the earthboundedness, of the Christ figure in this and other similar sculptures by Barthé distances it from its prototype, whereas I would counter that these very qualities mark Christ not just in scripture and creed but in centuries worth of passion imagery that reminds us of Christ’s suffering in the flesh (visible indicators of divinity or transcendence were not always present). And as for the exposed genitalia, Renaissance artists often used this device in paintings of the infant Christ as a way of asserting his full humanity. While I find Smalls’s thesis unconvincing, I nevertheless appreciate the attention he sheds on this artist who was new to me.
In chapter 8, Julie Levin Caro shows how Allan Rohan Crite’s serial drawings of Negro spirituals “refute the stereotypical tropes of the spirituals as the embodiment of a southern, black folk sensibility or the atavistic religious practices of slaves” (104), instead showing them enacted by contemporary, well-to-do, black Episcopalians in Boston, of which Crite was one. He wanted to reclaim the spirituals as religious “hymns,” part of the canons of Western liturgical music and concert music, and in his attempt to portray them as sophisticated, in his drawing captions (comprising lyric excerpts) he purged the vernacular English and wrote in a Gothic-inspired font. “Crite’s particular contribution to the history of American religious art challenges a bias within the discourse on racial identity in art that privileges an essentialized conception of black religious identity centered upon the ‘folk,’ or working- and lower-class African Americans, and a southern-based evangelical or fundamental style of worship” (111); here, instead, is the black middle class engaged in liturgical worship in the North.
In chapter 9, Elaine Y. Yau examines the visionary art of Sister Gertrude Morgan, who in 1957 was, by her own account, crowned the bride of Christ. At a time when interracial marriages were frowned upon, she represented herself, through numerous crayon drawings with scribbled text, standing in a white wedding dress alongside a white Jesus.
In chapter 10, Edward M. Puchner sheds light on the salvaged limestone sculptures of Nashville stone carver William Edmondson, who started sculpting in response to a command he received from God in a vision, filling his backyard with Crucifixions, angels, animals, preachers, and public figures. Museum of Modern Art director Alfred Barr’s interest in Edmondson’s work, which he classified as “modern primitive,” led to a solo exhibition at the MoMA in 1937 (he was the first African American to receive that honor). Until his death, Edmondson maintained a tombstone carving business and a modernist sculpture studio, fulfilling the needs of two separate audiences. Puchner focuses on the artist’s personal religious convictions, often overlooked in scholarship, as a key to understanding his art, and spends the most time on his Crucifixion.
In chapter 11, Richard J. Powell discusses Horace Pippin’s ten biblical paintings, most notably his Holy Mountain series inspired by Edward Hicks’s Peaceable Kingdom paintings.
In chapter 12, Carla Williams discusses James VanDerZee’s photographs of churches as service and social organizations within the Harlem community, and of black religious leaders. She contrasts his double-exposed Daddy Grace (1938), a flamboyant celebrity preacher of the prosperity gospel depicted on a stage before throngs of worshippers, with Barefoot Prophet (Elder Clayhorn Martin) (1929), a modest and unassuming follower of God who is depicted alone, deep in prayer before an open Bible and a crucifix.
In chapter 13, Kymberly N. Pinder examines key works from Romare Bearden’s 1945 Passion of Christ series, questioning whether abstraction is a fitting vehicle for religious themes. The essay contains several quotes from the artist and places him in a larger context of twentieth-century religious painting. It’s frustrating that of the three Bearden paintings reproduced in the chapter—Madonna and Child (1945), The Visitation (1941) and He Is Arisen (1945), though all compelling in their own right—only the latter is from his Passion series, the essay’s focus, and even then, it’s not a passion subject.
In chapter 14, Kristin Schwain looks at how Jacob Lawrence, when commissioned to illustrate the first chapters of Genesis, chose to visualize a black preacher’s evocation of the narrative for his parishioners (that is, its oral performance) rather than the written text itself. The sermonic invocation conjures biblical imagery of the different stages of creation in the four arcade windows in the background. These eight gouaches were inspired by Adam Clayton Powell Sr., the senior pastor of Harlem’s Abyssinian Baptist Church, where Lawrence attended. Each contains the same five elements—a preacher at the pulpit, a congregation in the pews, a set of windows, a box of carpentry tools, and a flower vase—but through creative variation, the composition avoids repetitiveness. (see the first one, In the beginning, all was void, on the book cover above)
More:
28 March 2024 / Stations of the Cross in HornseaMatthew Askey's most recent project is a set of ‘Stations of the Cross’ for St Nicholas Church, Hornsea. This is a site-specific commission of paintings that link each Station to a part of the town.
Read more...28 February 2024 / Book review Abundantly More
01 February 2024 / James Tughan: CONTACT
13 October 2023 / David Miller Interview
“Form welcomes the formless home”
Jonathan Evens interviews David Miller on his work and the “interrelation, symbiosis and overlap” between writing and visual art
Read more...07 August 2023 / Ethnoarts Scripture Engagement
by Scott Rayl
Ethnoarts are artistic ‘languages’ that are unique to a particular community. They can help strengthen cultural and Christian identity.
Read more...12 June 2023 / Georges Rouault and André Girard
by Jonathan Evens
Rouault and Girard: Crucifixion and Resurrection, Penitence and Life Anew
Read more...28 April 2023 / Josh Tiessen: Vanitas + Viriditas
28 April - 26 May, New York gallery Rehs Contemporary will present Josh Tiessen: Vanitas and Viriditas.
Read more...10 April 2023 / Images for God the Father
by Marleen Hengelaar-Rookmaaker
How can we ever comprehend God the Father with our small human intellects? How can we ever get to know Him and learn to live with Him?
Read more...16 February 2023 / Ervin Bossanyi: A vision for unity and harmony
by Jonathan Evens
Bossanyi joined the large number of émigré artists arriving in Britain after WW II, many of whom were Jewish and explored spirituality within their work.
Read more...06 January 2023 / The Creative Process
by Colin Black
Creative journeys are full of mishaps, accidents, and wrong turnings.
Read more...01 December 2022 / ArtWay newsletter 2022
Artway will be continued by the Kirby Laing Centre for Public Theology from the beginning of 2024.
Read more...20 October 2022 / Kuyper, the Aesthetic Sphere, and Art
After three centuries of silence about art in Reformed theological circles in the Netherlands, suddenly there was Abraham Kuyper, whose great merit it was that he once again drew attention to art.
Read more...06 September 2022 / On the Street: The work of JR
by Betty Spackman
Through the project in Tehachapi JR wanted to "give voice to prisoners" and humanize their environment.
Read more...04 August 2022 / Joseph Beuys: A Spiritual German Artist
Is there a thread that connects the multifaceted work of this artist? My hypothesis is that Beuys’ spirituality is what drives his diverse work.
Read more...01 June 2022 / Interview with Belinda Scarlett
BELINDA SCARLETT, theatre costume and set designer and ecclesiastical textile artist
Interview by JONATHAN EVENS
Read more...21 April 2022 / Betty Spackman: A Creature Chronicle
When I consider the heavens, the moon and the stars that you have made, what are mere mortals that you are mindful of them… Psalm 8
Read more...08 April 2022 / Historical Models for Crosses and Crucifixes Today
All crosses and crucifixes symbolise joy and salvation. But formally there are two different types: the victorious and the suffering crucifix.
Read more...16 March 2022 / Three artworks by Walter Hayn
by Gert Swart
These three artworks must have turned Walter Hayn inside out, being so powerfully revealing.
Read more...22 February 2022 / Abstract Expressionism
by Nigel Halliday
It is worth the while to remember the deep seriousness of these artists – even if their suggested answers can look sadly thin.
Read more...07 January 2022 / Artist duo Gardner & Gardner
by Elizabeth Kwant
During COP26 artist duo Gardner & Gardner installed their work I will learn to sit with you and I will learn to listen in Glasgow Cathedral.
Read more...09 December 2021 / ArtWay Newsletter and List of Books 2021
Marleen Hengelaar-Rookmaaker intends to phase out her participation in the day to day oversight of the ArtWay website over the course of the coming new year.
Read more...03 November 2021 / The Seven Works of Mercy in Art
by Marleen Hengelaar-Rookmaaker
This overview will show that these artworks from different ages mirror the theological ideas and the charitable works of their times.
Read more...06 October 2021 / Disciplining our eyes with holy images
by Victoria Emily Jones
Images tend to work a subtle magic on us, especially after years of constant exposure.
Read more...24 August 2021 / On the Gifts of Street Art
by Jason Goroncy
These works represent an act of reclaiming public space for citizens rather than merely consumers.
Read more...27 July 2021 / Russia’s 1st Biennale of Christ-centered Art
An opportunity of dialogue between the church and contemporary art
by Viktor Barashkov
Read more...30 June 2021 / Jacques and Raïssa Maritain among the Artists
by David Lyle Jeffrey
About the influence of Jacques and Raïssa Maritain on Rouault, Chagall and Arcabas.
Read more...13 May 2021 / GOD IS...
Chaiya Art Awards 2021 Exhibition: “God Is . . .”
by Victoria Emily Jones
Read more...21 April 2021 / Photographing Religious Practice
by Jonathan Evens
The increasing prevalence of photographic series and books exploring aspects of religious practice gives witness to the return of religion in the arts.
Read more...23 March 2021 / Constanza López Schlichting: Via Crucis
Perhaps what may be different from other Stations of the Cross is that it responds to a totally free expression and each station is a painting in itself.
Read more...10 February 2021 / Gert Swart: Four Cruciforms
In a post-Christian era, contemporary Christian artists have to find new ways of evoking the power of the cross.
Read more...08 January 2021 / Reflecting on a Gauguin Masterpiece
by Alan Wilson
An artist's reflection on Impressionism, Cezanne, Van Gogh and especially Gauguin's Vision after the Sermon.
Read more...11 December 2020 / ArtWay Newsletter 2020
What makes the ArtWay platform so special is its worldwide scope thanks to its multilingual character. There are ArtWay visitors in all countries on this planet.
Read more...27 October 2020 / Art Pilgrimage
A Research Project on Art Stations of the Cross
by Lieke Wijnia
Read more...18 September 2020 / Interview with Peter Koenig
by Jonathan Evens
Koenig's practice demonstrates that the way to avoid blandness in religious art is immersion in Scripture.
Read more...17 August 2020 / BOOK REVIEW BY HEINRICH BALZ
How Other Cultures See the Bible
Christian Weber, Wie andere Kulturen die Bibel sehen. Ein Praxisbuch mit 70 Kunstwerken aus 33 Ländern.
Read more...17 July 2020 / The Calling Window by Sophie Hacker
by Jonathan Evens
In 2018 British artist Sophie Hacker was approached to design a window for Romsey Abbey to celebrate the bicentenary of the birth of Florence Nightingale.
Read more...12 June 2020 / A little leaven leavens the whole lump
From South Africa
Ydi Carstens reports on the group show ‘Unleavened’ which was opened in Stellenbosch shortly before the Covid-19 lock-down.
Read more...14 May 2020 / Jazz, Blues, and Spirituals
Republished:
Hans Rookmaaker, Jazz, Blues, and Spirituals. The Origins and Spirituality of Black Music in the United States.
Reviewed by Jonathan Evens
Read more...17 April 2020 / Andy Warhol: Catholicism, Work, Faith And Legacy
by Jonathan Evens
While Warhol’s engagement with faith was complex it touched something which was fundamental, not superficial.
Read more...25 March 2020 / Sacred Geometry in Christian Art
by Sophie Hacker
This blog unravels aspects of sacred geometry and how it has inspired art and architecture for millennia.
Read more...22 February 2020 / Between East and West
By Kaori Homma
Being in this limbo between day and night makes me question, “Where does the east end and the west start?”
Read more...15 February 2020 / Imagination at Play
by Marianne Lettieri
To deny ourselves time to laugh, be with family and friends, and fuel our passions, we get caught in what Cameron calls the “treadmill of virtuous production.”
Read more...07 December 2019 / ArtWay Newsletter 2019
An update by our editor-in-chief
and
the ArtWay List of Books 2019
16 November 2019 / Scottish Miracles and Parables Exhibition
Alan Wilson: "Can there be a renewal of Christian tradition in Scottish art, where ambitious artists create from a heartfelt faith, committed to their Lord and saviour as well as their craft?"
Read more...23 September 2019 / Dal Schindell Tribute
While Dal’s ads and sense of humour became the stuff of legends, it was his influence on the arts at Regent College in Vancouver, Canada that may be his biggest legacy.
Read more...04 September 2019 / The Aesthetics of John Calvin
Calvin stated that 'the faithful see sparks of God's glory, as it were, glittering in every created thing. The world was no doubt made, that it might be the theater of divine glory.'
Read more...31 July 2019 / The Legend of the Artist
by Beat Rink
The image of the 'divine' artist becomes so dominant that artists take their orientation from it and lead their lives accordingly.
Read more...02 July 2019 / Quotes by Tim Keller
Many “Christian art” productions are in reality just ways of pulling artists out of the world and into the Christian subculture.
Read more...08 June 2019 / The Chaiya Art Awards
by Jonathan Evens
The Chaiya Art Awards 2018 proved hugely popular, with over 450 entries and more than 2,700 exhibition visitors.
Read more...29 May 2019 / Art Stations of the Cross: Reflections
by Lieke Wynia
In its engagement with both Biblical and contemporary forms of suffering, the exhibition addressed complex topical issues without losing a sense of hope out of sight.
Read more...03 May 2019 / Marianne Lettieri: Relics Reborn
Items that show the patina of time and reveal the wear and tear of human interaction are carriers of personal and collective history.
Read more...27 April 2019 / Franciscan and Dominican Arts of Devotion
by John Skillen
This manner of prayer stirs up devotion, the soul stirring the body, and the body stirring the soul.
Read more...13 March 2019 / Makoto Fujimura and the Culture Care Movement
by Victoria Emily Jones
Culture care is a generative approach to culture that brings bouquets of flowers into a culture bereft of beauty.
Read more...08 January 2019 / Building a Portfolio of People
by Marianne Lettieri
Besides hard work in the studio, networking may be the single most important skill for a sustainable art practice.
Read more...01 December 2018 / ArtWay Newsletter December 2018
ArtWay has Special Plans for 2019!
After London, Washington D.C. and New York the city of Amsterdam in the Netherlands is now the anticipated location for a prominent art exhibition with the title Art Stations of the Cross.
Read more...11 October 2018 / The Life, Art and Legacy of Charles Eamer Kempe
Book Review by Jonathan Evens
The significance and spirituality of the work is made clear in ways which counteract the stereotype of mass production of a static style.
Read more...13 September 2018 / A Visit to the Studio of Georges Rouault
by Jim Alimena
Everything we saw and learned reinforced my picture of a great man of faith and a great artist.
Read more...09 August 2018 / With Opened Eyes: Representational Art
by Ydi Coetsee
How do we respond to the ‘lost innocence’ of representational art?
Read more...13 July 2018 / True Spirituality in the Arts
by Edith Reitsema
Living in Christ should lead us away from living with a segregated view of life, having a sacred-secular split.
Read more...23 April 2018 / Short Introduction to Hans Rookmaaker
by Marleen Hengelaar-Rookmaaker
On the occasion of the establishment of the Rookmaaker Jazz Scholarship at Covenant College, Chattanooga, Tennessee, 12 March 2018
Read more...04 April 2018 / International Art Residency in India
Art for Change, a New Delhi based arts organization with a vision to see art shape society with beauty and truth, will be running its 6th annual International Artist Residency in November 2018.
Read more...15 March 2018 / The Stations of the Cross at Blackburn Cathedral
by Penny Warden
Perhaps the central challenge for the artist in imaging the body of Christ is the problem of representing the dual natures of the doctrine of the incarnation.
Read more...23 February 2018 / Between the Shadow and the Light
By Rachel Hostetter Smith
In June 2013 a group of twenty North American and African artists from six African countries met for two weeks of intensive engagement with South Africa.
Read more...30 January 2018 / Sacred Geometry in Christian Art
by Sophie Hacker
This blog unravels aspects of sacred geometry and how it has inspired art and architecture for millennia.
Read more...01 January 2018 / Jonathan Evens writes about Central Saint Martins
Why would Central Saint Martins, a world-famous arts and design college and part of University of the Arts London, choose to show work by its graduates in a church?
Read more...06 December 2017 / ArtWay Newsletter December, 2017
ArtWay's Chairman Wim Eikelboom: "The visual arts cultivate a fresh and renewed view of deeply entrenched values. That is why ArtWay is happy to provide an online platform for art old and new."
Read more...14 November 2017 / The Moral Imagination: Art and Peacebuilding
In the context of conflict transformation the key purpose of creative expression is to provide a venue for people to tell their stories, and for their stories to be heard.
Read more...24 October 2017 / Bruce Herman: Ut pictura poesis?
For the last couple hundred of years the arts have largely been in "experimentation mode"—moving away from the humble business of craft and service toward ideas, issues, and theory.
Read more...04 October 2017 / David Jeffrey: Art and Understanding Scripture
The purpose of In the Beauty of Holiness: Art and the Bible in Western Culture is to help deepen the reader’s understanding of the magnificence of the Bible as a source for European art.
Read more...08 September 2017 / David Taylor: The Aesthetics of John Calvin
Calvin stated that 'the faithful see sparks of God's glory, as it were, glittering in every created thing. The world was no doubt made, that it might be the theater of divine glory.'
Read more...23 August 2017 / Reconstructed by Anikó Ouweneel
A much talked-about exposition in the NoordBrabants Museum in The Netherlands showed works by modern and contemporary Dutch artists inspired by traditional Catholic statues of Christ and the saints.
Read more...04 July 2017 / Pilgrimage to Venice – The Venice Biennale 2017
When I start to look at the art works, I notice a strange rift between this pleasant environment and the angst and political engagement present in the works of the artists.
Read more...24 June 2017 / Collecting as a Calling
After many years of compiling a collection of religious art, I have come to realize that collecting is a calling. I feel strongly that our collection has real value and that it is a valuable ministry.
Read more...02 June 2017 / I Believe in Contemporary Art
By Alastair Gordon
In recent years there has been a growing interest in questions of religion in contemporary art. Is it just a passing fad or signs of renewed faith in art?
Read more...04 April 2017 / Stations of the Cross - Washington, DC 2017
by Aaron Rosen
We realized that the Stations needed to speak to the acute anxiety facing so many minorities in today’s America and beyond.
Read more...07 March 2017 / Socially Engaged Art
A discussion starter by Adrienne Dengerink Chaplin
Growing dissatisfaction with an out-of-touch, elite and market driven art world has led artists to turn to socially engaged art.
Read more...01 February 2017 / Theodore Prescott: Inside Sagrada Familia
The columns resemble the trunks of trees. Gaudi conceived of the whole interior as a forest, where the nave ceiling would invoke the image of an arboreal canopy.
Read more...03 January 2017 / Steve Scott tells about his trips to Bali
In the Balinese shadow play the puppet master pulls from a repertoire of traditional tales and retells them with an emphasis on contemporary moral and spiritual lessons.
Read more...09 December 2016 / Newsletter ArtWay December 2016
Like an imitation of a good thing past, these days of darkness surely will not last. Jesus was here and he is coming again, to lead us to the festival of friends.
Read more...01 November 2016 / LAbri for Beginners
What is the role of the Christian artist? Is it not to ‘re-transcendentalise’ the transcendent, to discern what is good in culture, and to subvert what is not with a prophetic voice?
Read more...30 September 2016 / Book Review by Jonathan Evens
Jonathan Koestlé-Cate, Art and the Church: A Fractious Embrace - Ecclesiastical Encounters with Contemporary Art, Routledge, 2016.
Read more...01 September 2016 / Review: Modern art and the life of a culture
The authors say they want to help the Christian community recognize the issues raised in modern art and to do so in ways that are charitable and irenic. But I did not find them so. Their representation of Rookmaaker seems uncharitable and at times even misleading.
Read more...29 July 2016 / Victoria Emily Jones on Disciplining our Eyes
There’s nothing inherently wrong with images—creating or consuming. In fact, we need them. But we also need to beware of the propensity they have to plant themselves firmly in our minds.
Read more...30 June 2016 / Aniko Ouweneel on What is Christian Art?
Pekka Hannula challenges the spectator to search for the source of the breath we breathe, the source of what makes life worth living, the source of our longing for the victory of redemptive harmony.
Read more...09 June 2016 / Theodore Prescott: The Sagrada Familia
Sagrada Familia is a visual encyclopedia of Christian narrative and Catholic doctrine as Gaudi sought to embody the faith through images, symbols, and expressive forms.
Read more...19 May 2016 / Edward Knippers: Do Clothes make the Man?
Since the body is the one common denominator for all of humankind, why do we fear to uncover it? Why is public nudity a shock or even a personal affront?
Read more...27 April 2016 / Alexandra Harper: Culture Care
Culture Care is an invitation to create space within the local church to invest our talents, time and tithes in works that lean into the Kingdom of God as creative agents of shalom.
Read more...06 April 2016 / Jonathan Evens on Contemporary Commissions
The issue of commissioning secular artists versus artists of faith represents false division and unnecessary debate. The reality is that both have resulted in successes and failures.
Read more...12 March 2016 / Betty Spackman: Creativity and Depression
When our whole being is wired to fly outside the box, life can become a very big challenge. To carve oneself into a square peg for the square holes of society, when you are a round peg, is painful to say the least.
Read more...24 February 2016 / Jim Watkins: Augustine and the Senses
Augustine is not saying that sensual pleasure is bad, but that it is a mixed good. As his Confessions so clearly show, Augustine is painfully aware of how easily he can take something good and turn it into something bad.
Read more...11 February 2016 / H.R. Rookmaaker: Does Art Need Justification?
Art is not a religion, nor an activity relegated to a chosen few, nor a mere worldly, superfluous affair. None of these views of art does justice to the creativity with which God has endowed man.
Read more...26 January 2016 / Ned Bustard: The Bible is Not Safe
Revealed is intended to provoke surprise, even shock. It shows that the Bible is a book about ordinary people, who are not only spiritual beings, but also greedy, needy, hateful, hopeful, selfish, and sexual.
Read more...14 January 2016 / Painting by Nanias Maira from Papua New Guinea
In 2011 Wycliffe missionary Peter Brook commissioned artist Nanias Maira, who belongs to the Kwoma people group of northwestern Papua New Guinea, to paint Bible stories in the traditional style for which he is locally known.
Read more...